Amylase (Alpha-amylase)
α-淀粉酶
HK$217.00
CAS : 9000-90-2
Brand : Macklin
Weight : 100g
Amylase is an important topic covered in the IB biology curriculum. Amylase is an enzyme that is primarily responsible for the digestion of starch, breaking it down into smaller sugar molecules. Specifically, the IB syllabus covers the following aspects of amylase:
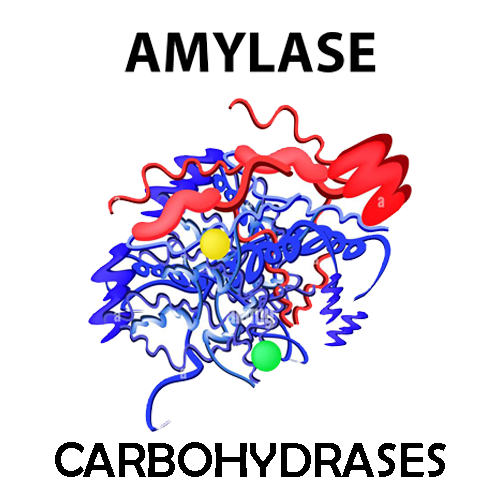
Structure and function of amylase: Amylase is a hydrolytic enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the α-1,4 glycosidic bonds in starch molecules, breaking them down into maltose and glucose. Students need to understand the 3D structure of amylase and its catalytic mechanism.
Role of amylase in the human digestive system: Amylase is secreted by the salivary glands and the pancreas, and it acts in the mouth and small intestine to digest starch in food. Students need to comprehend the function of amylase in the human digestive process.
Experimental methods to measure amylase activity: Students often perform experiments to measure the activity of amylase, such as using starch solution as a substrate and determining the rate of starch hydrolysis over time. This helps students understand the catalytic mechanism of amylase.
Factors affecting amylase activity: Students need to learn how factors like pH and temperature can influence the catalytic activity of amylase. This aids in the understanding of the characteristics of biological enzymes.
Applications of amylase in biotechnology: Amylase has widespread applications in the food processing and medical industries, and students need to be aware of these applications.
Amylase is a crucial topic in the IB biology syllabus, covering aspects related to enzyme structure, function, catalytic mechanisms, and experimental determination.

